Conventional Road Guide Signs: Proportion Based Grid System
The 2004 Interim Approval (IA-5) allowed states and local jurisdictions to use the Clearview Type System in positive contrast applications. This was a significant change as guide sign layouts since 1961 were specified using all uppercase legends with FHWA Series D legends in fixed blocks of type.
The conventional road guide sign formats we developed provide state and local DOTs grid formats to uniformly accommodate legends with descending characters (g, j, p, q and y) in single line (one destination) signs or in complex layouts with three destinations and supporting graphic elements regardless of sign size.
Clearview 3-W typeface was found to improve legibility and glance recognition when compared to uppercase legends in Series D and to FHWA Series D mixed case fonts. Research showed Clearview 3-W to be 29 percent more legible in daytime viewing and 22 percent more legible at night in older driver studies when compared to same weight mixed case FHWA Series D font (see case study 3 in research section of this site).
Combining typeface improvements with consistent panel layouts allows the motorist to recognize a specific destination on a guide sign from a longer distance and read it at a glance more quickly. The motorists, attention can return to the road in the shortest time possible.
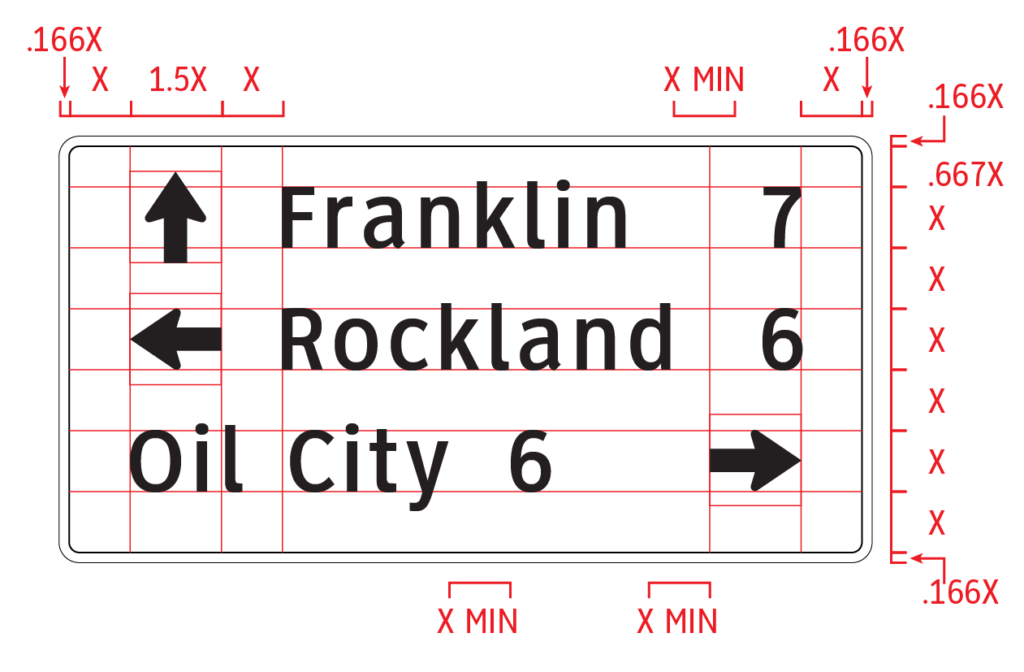
Grids are based on a consistent set of rules and simple mathematical proportions (X) where (X) is the primary legend capital letter height. Layouts may include: symbols, arrows, route shields, cardinal directions, secondary legends, interline space (single line or return line), numbers and fractions, the surrounding field and borders; all using the single set of rules regardless of primary legend size and all based on clean mathematical relationships.
The common figure/field relation will also allow all signs of a type to be made in a precisely consistent format, regardless of their size or complexity. In fact, all sign layouts can be prepared at the same scale and simply enlarged as a vector file to the size required. Digitally printed signs are precisely segmented based on sheeting width affording flawless edge lay-up. The layout of applied legends is simplified as the rules are consistent.
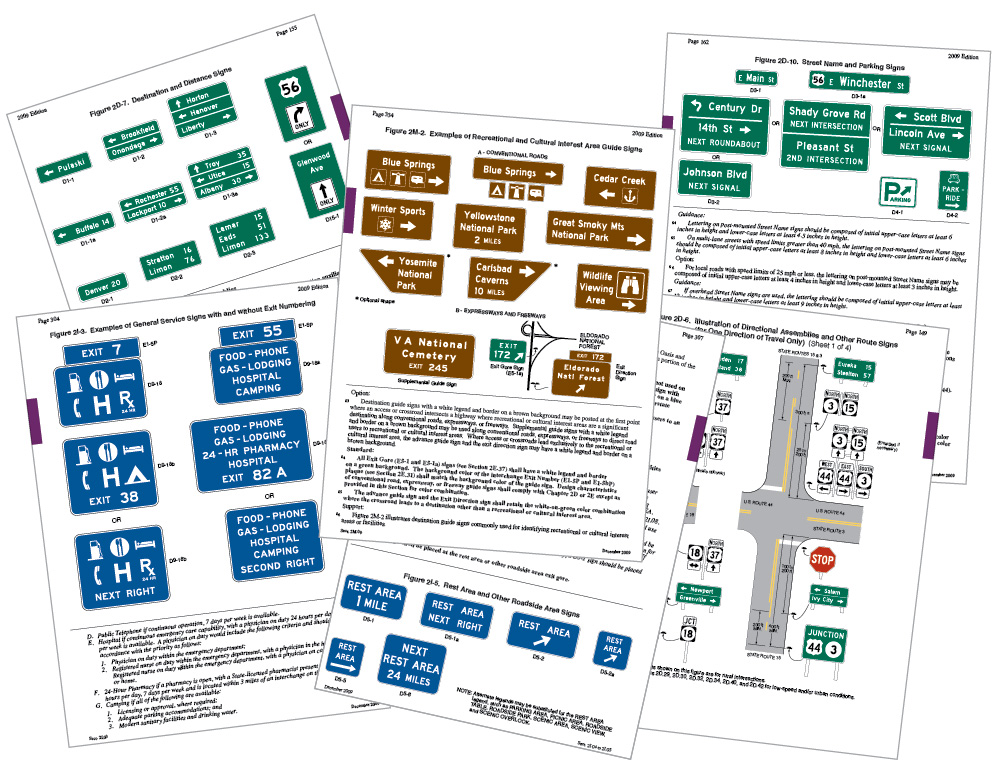
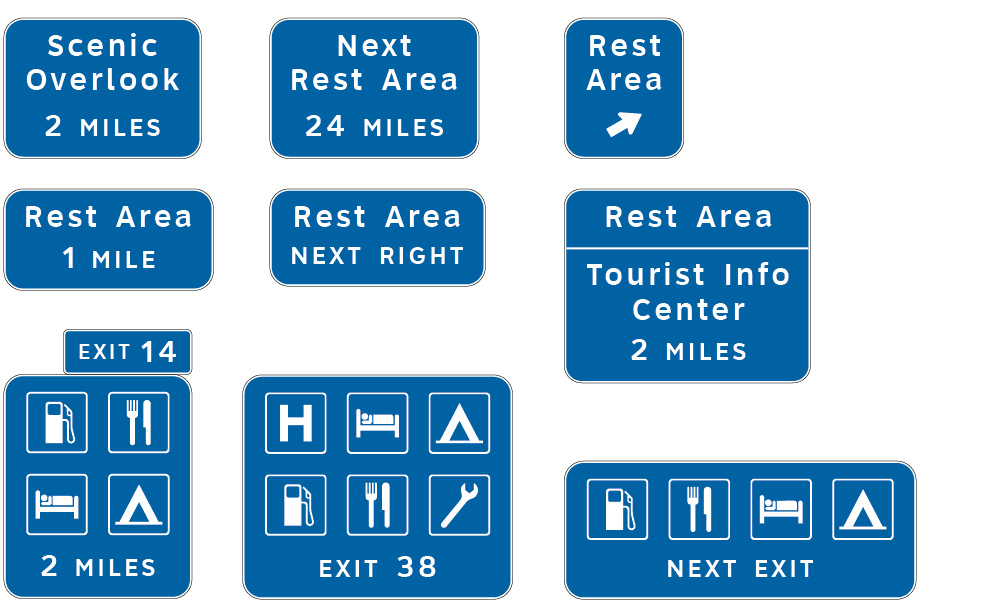
In developing a proportion-based approach to sign layout, we identified an opportunity to include related guide and information signs. This simplifies what has historically been a similar but different set of layouts as shown above in pages from the MUTCD for: Recreational and Cultural Interest Area Guide Signs, Recreation Symbols Guide Signs, General Service Signs, Rest Area and Other Roadside Area Signs and Route Shields on Universal Backers. Consistency, uniformity, let alone improved readability aids all drives and reduces planning and production costs.
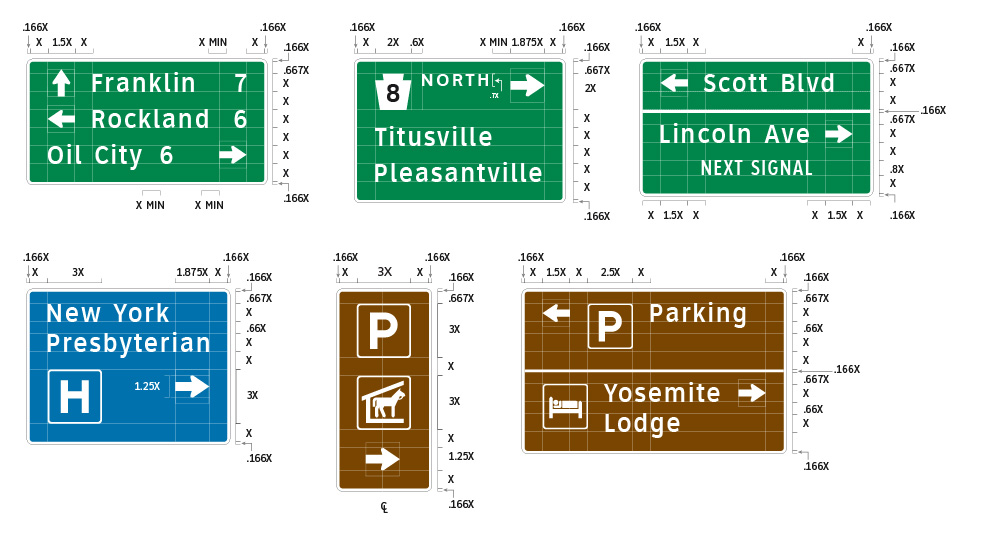
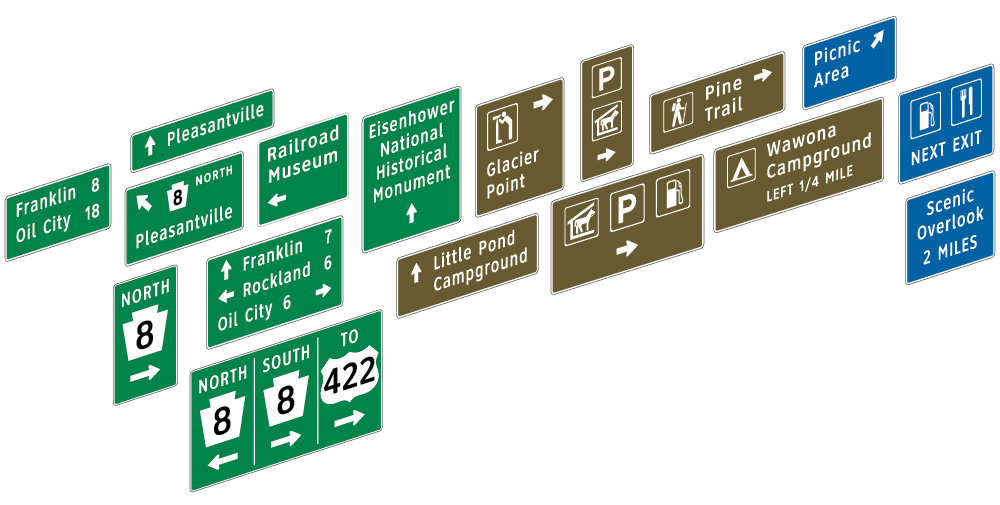
Guidance and motorist information should be an integrated system adapted proportionally. Mixed case legends, these are adaptable to common figure and field relationships and differ only in color. Sign types include:
- Recreational and Cultural Interest Area Guide Signs
- Recreation Symbols Guide Signs
- General Service Signs
- Rest Area and Other Roadside Area Signs
- Route Shields on Universal Backers
Conventional Road Guide Signs
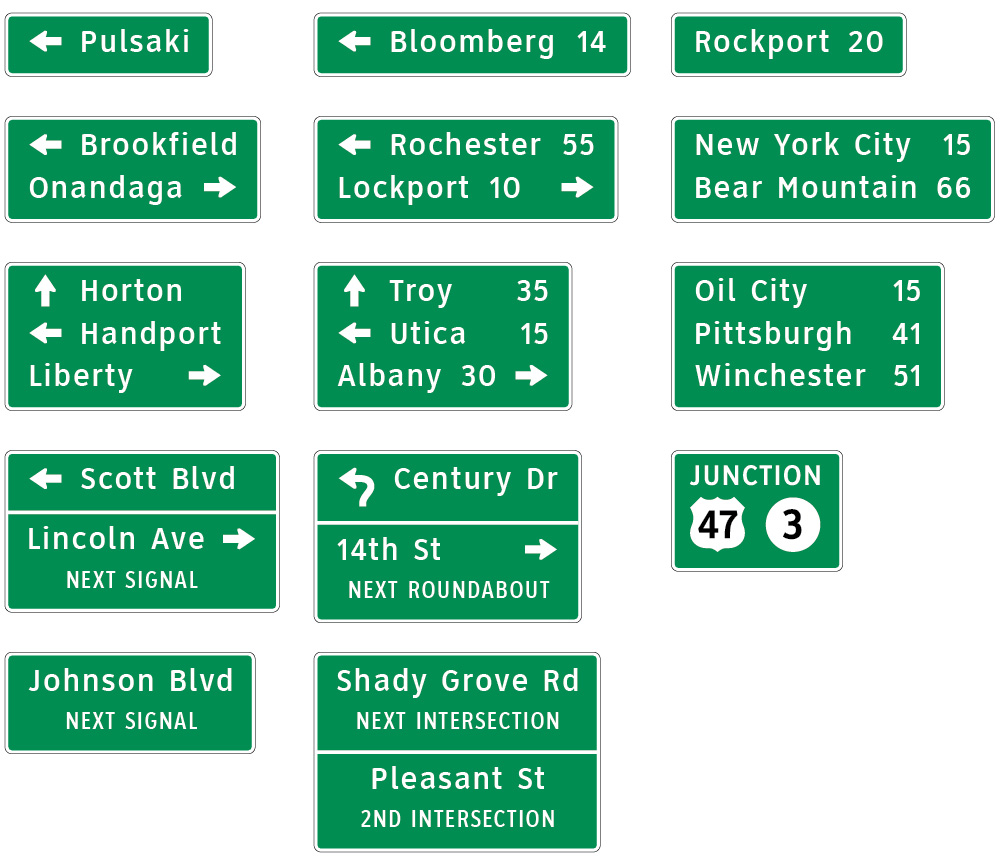
Recreational and Cultural Area Interest Signs for conventional roads
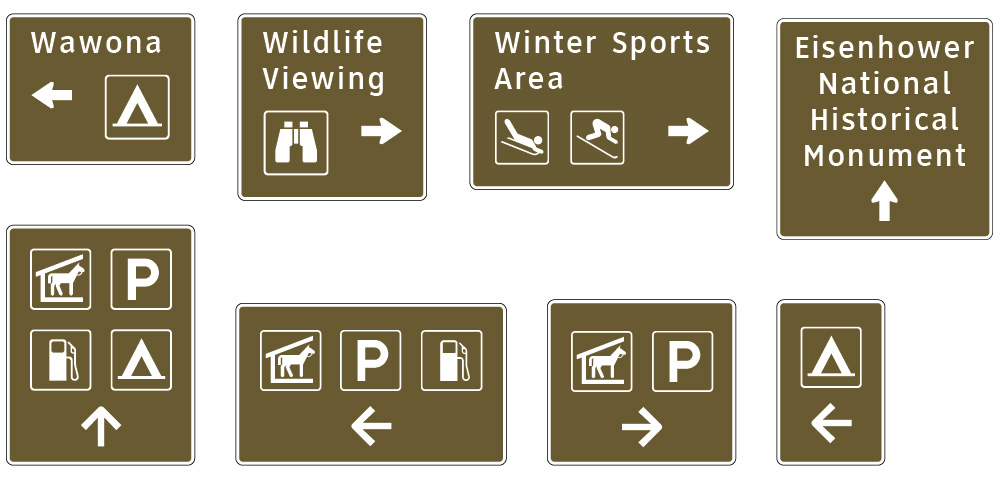
General Service Signs and Rest Area and other Roadside Area Signs
Route Shields on Universal Backers
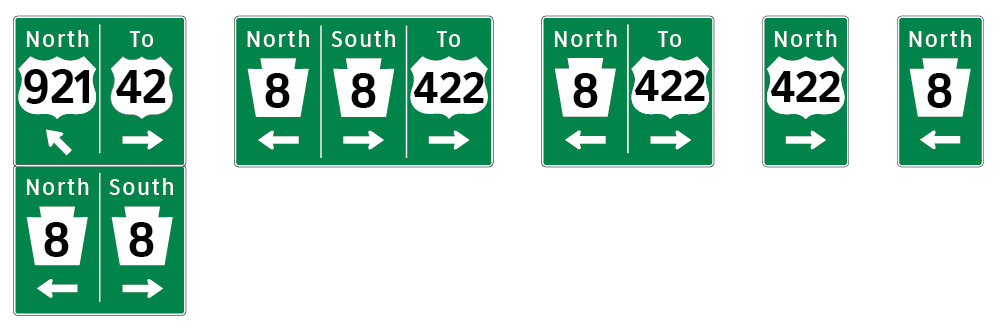
Route shields are generally comprised of three modules: cardinal direction panel; route shield and arrow panel. The existing mountings for shields, a tangle of metal channel, angle sections and straps, are clumsy, unattractive and inefficient.
A new design groups the applied modules on a universal (pre-drilled) backer, drilled and top coated, with sheeting sized to accommodate different shields. The uniformly designed backer and panels are more clearly ordered than existing mountings and save installation time. (We learned that some entities such as the Maryland State Highway Administration (MSHA) created their own effective solutions for backers.) The example (show above) uses a green universal backer to enhance “positive guidance.” Updated universal backer design can simplify layouts for all guide and informational signs in the MUTCD.
D. Meeker, M. Pietrucha, P. Garvey., Proportion Based Format System for Conventional Road Guide Signs., Presented at TRB Annual Meeting (2006), Transportation Research Record No. 1973, NRC/ TRB. Washington, D.C. (2006).
